immune cell interactions in physiology and pathology Immunity Biology Diagrams
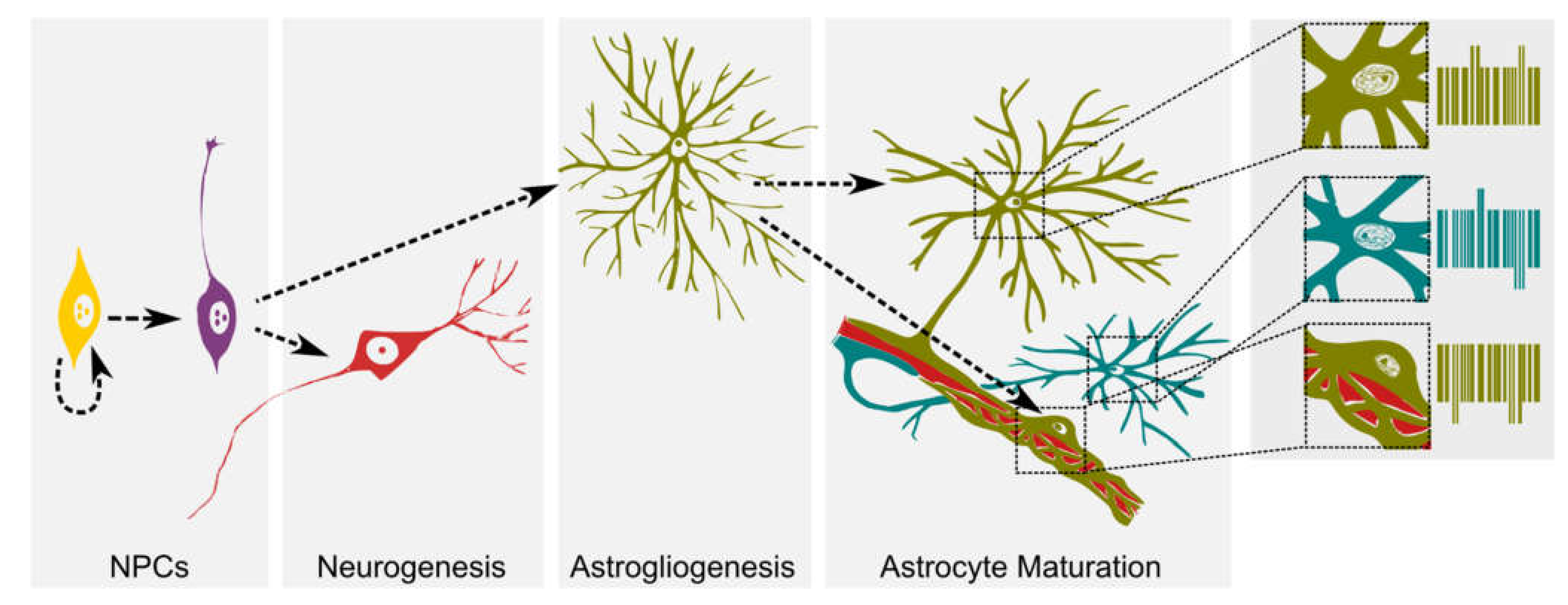
immune cell interactions in physiology and pathology Immunity Biology Diagrams Astrocytes are the most abundant cell type in the central nervous system and have diverse functions in blood-brain barrier maintenance, neural circuitry formation and function, and metabolic regulation. To better understand the diverse roles of astrocytes, we will summarize what is known about astrocyte development and the challenges limiting Astrocytes are a subtype of glial cells that make up the majority of cells in the human central nervous system (CNS). They perform metabolic, structural, homeostatic, and neuroprotective tasks such as clearing excess neurotransmitters, stabilizing and regulating the blood-brain barrier, and promoting synapse formation.[1][2][3][4] Unlike neurons and other cells in the nervous system, they do Introduction. Astrocytes comprise a diverse population of cells responsible for a broad array of functions in the nervous system. Nevertheless, our understanding of fundamental principles of astrocyte biology, including their development, remains far behind that of other glial cell populations in the nervous system, including oligodendrocytes and Schwann cells (Jessen and Mirsky, 2005).

Astrocytes are the most abundant cell type in the central nervous system and have diverse functions in blood-brain barrier maintenance, neural circuitry formation and function, and metabolic regulation. These parental cells exhibited astrocyte characteristics, including morphology, gap junction connectivity, and expression of astrocyte

Histology, Astrocytes Biology Diagrams
Astrocytes represent a transcriptomically, morphologically, and (likely) functionally heterogeneous cell population in the vertebrate CNS. Early observations of heterogeneity relied on morphology, and astrocytes were divided into two broad subtypes: gray matter astrocytes with a protoplasmic morphology and white matter astrocytes that have a fibrous morphology. 30 While useful in the early Astrocytes are a heterogeneous population of cells with distinguishing functional and morphological characteristics and are specialized to their different brain regions and locations. 4 Regional
The GO terms for cluster 5 are related to cell cycle and proliferation processes, A primary objective of this study was to understand the distinctive characteristics of WM astrocytes. Unlike The source of newly divided scar-forming astrocytes is not well established, and may include mature astrocytes that re-enter the cell cycle as well as progenitor cells in the local parenchyma or in the periventricular regions [30, 33, 37, 77, 133, 141, 226]. Molecular triggers and regulators of reactive astrogliosis and glial scar formation Astrocytes are the most plentiful cell type in the central nervous system (CNS) and perform complicated functions in health and disease. It is obvious that different astrocyte subpopulations, or activation states, are relevant with specific genomic programs and functions. In recent years, the emergence of new technologies such as single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) has made substantial
