Centromeres and Kinetochores Cell Biology Diagrams
Centromeres and Kinetochores Cell Biology Diagrams Kinetochore proteins can be grouped according to their concentration at kinetochores during mitosis: some proteins remain bound throughout cell division, whereas some others change in concentration. Furthermore, they can be recycled in their binding site on kinetochores either slowly (they are rather stable) or rapidly (dynamic). During mitosis, it's up to the kinetochores assembled on the centromeres of each chromosome to give a cell the go-ahead to begin anaphase. A kinetochore will only give its ready signal once it becomes attached to and stretched apart by microtubules emanating from both opposing spindle poles. This process, known as the spindle checkpoint, ensures the even distribution of chromosomes between
00115-6/asset/b4cb2bf2-5ae9-4290-a903-a2eb85b8405b/main.assets/gr6_lrg.jpg)
Introduction During mitosis, sister chromatids are segregated to the two daughter cells. This process requires the interaction between specialized chromosomal structures (kinetochores) and polymers of alpha- and beta-tubulin called microtubules.

Kinetochore structure and function Biology Diagrams
381 Kinetochore function: molecular motors, switches and gates Tim J Yen* and Bruce T Schaart Kinetochores are essential for accurate chromosome grow and shorten in a coordinated fashion to move the segregation. Recent studies reveal that vertebrate chromosome throughout mitosis (see Fig. 1 and [6-8]). kinetochores are sophisticated propulsion systems composed This bidirectional movement of
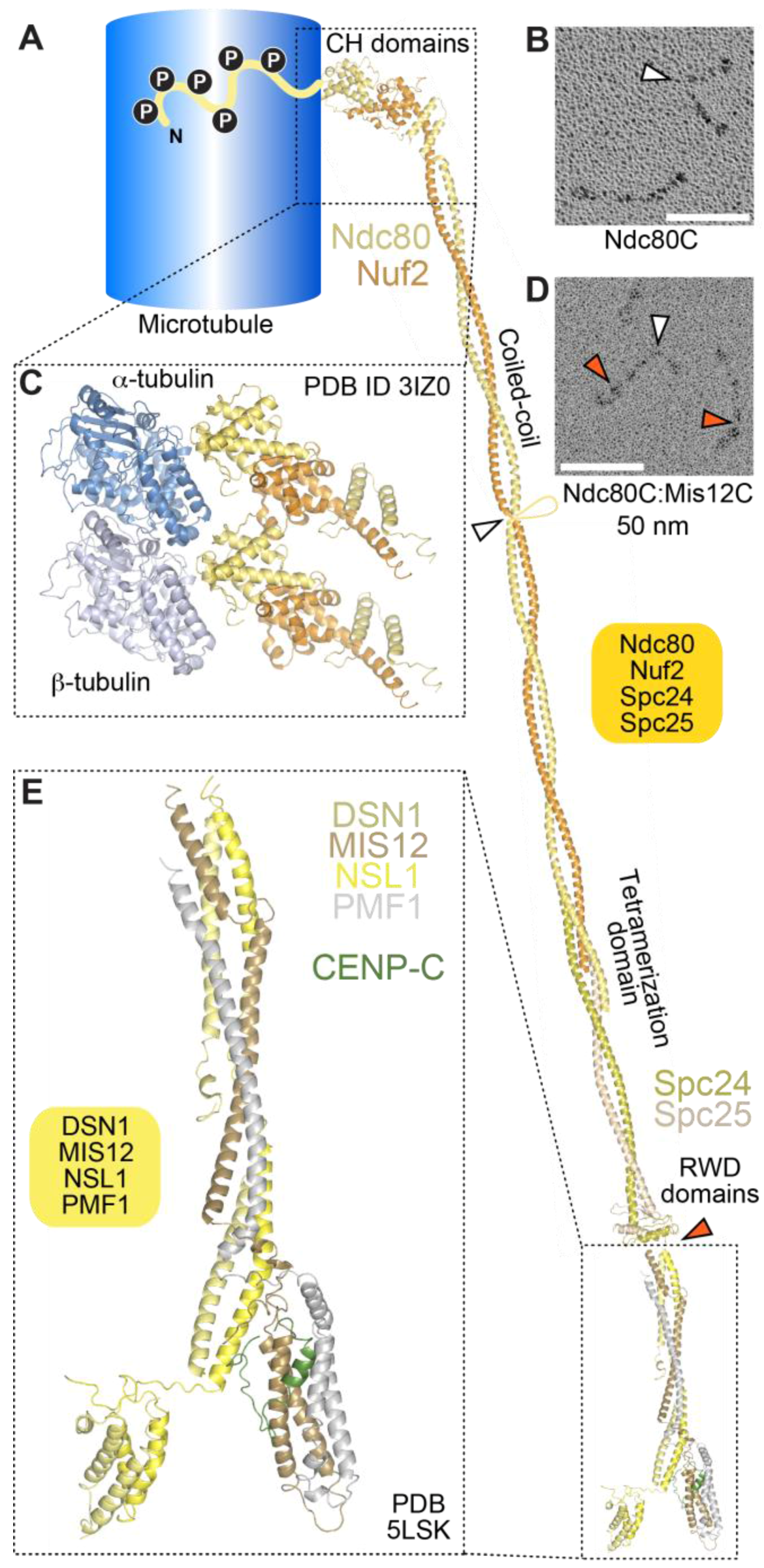
At the onset of mitosis, rapidly growing and shrinking microtubules (MTs) probe the cytoplasm in search of kinetochores, which are macromolecular complexes assembled on opposite sides of the centromere that mediate interactions between the chromosomes and MTs.
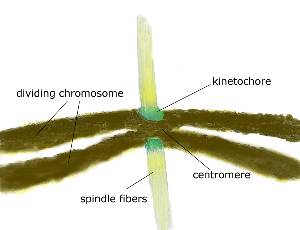
Sue Biggins: How kinetochores keep control of mitosis Biology Diagrams
In mitosis, chromosomes condense and the two copies become visible as "sister chromatids". One kinetochore is assembled on each of the two sister chromatids of a chromosome, and both sister kinetochores become attached to opposite spindle poles by metaphase.